The rate of residual urine in the bladder. How to get rid of residual urine in the bladder folk remedies? Increased residual urine volume in women
The human urinary system is formed in such a way that in a healthy body, after the act of urination, a small amount of urine remains in the bladder. It is called residual urine. This is an important indicator of the correct functioning of this system, since if the amount of residual urine greatly exceeds the norm, this indicates a serious pathology.
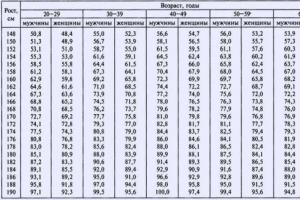
The rate of residual urine in the bladder
The amount of residual urine is highly dependent on physiological parameters such as gender and age. For example, in men, this rate is higher than in women, due to the larger volume of the bladder.
Table: acceptable indicators of residual urine in different categories of people
It should be noted that the values shown in the table are indicative. A slight deviation from these indicators does not at all indicate the presence of any pathology of the lower urinary tract. The main criterion for the norm when calculating residual urine is its content in the bladder in an amount of not more than 10% of the total volume of the organ cavity.
Causes of Excess Residual Urine
The appearance of excess residual urine can cause and provoke many diseases and disorders:
In addition to the above, organ injuries, surgical interventions, and systemic pathologies can lead to the occurrence of pathology.
Symptoms of a large volume of residual urine
The main signs indicating that the bladder is not completely emptied are:
- discomfort in the lower abdomen and groin;
- pains of a breaking nature;
- urge to urinate again;
- feeling of dissatisfaction with the act of urination.
The above signs are specific for this disorder, but given the fact that the formation of excess residual urine is not an independent pathology, but only a consequence of other diseases of the genitourinary system, the symptoms that belong to them come first:
- sensation of pain, burning and itching during the act of urination;
- a small, intermittent stream of urine;
- change in the color of urine, the presence of blood and pus in it.
Condition Diagnostics
When the amount of residual urine in the bladder slightly exceeds the physiological norm, this condition does not manifest itself with any symptoms. At this stage, it is almost impossible to suspect a pathology. The presence of this disorder, as a rule, is detected by the results of examinations associated with other diseases (prostatitis, cystitis), when the disease becomes severe. In this case, a medical examination is usually carried out as prescribed by a urologist or gynecologist. The main diagnostic methods include:

How to determine the volume of residual urine
The above studies are aimed at diagnosing diseases that cause excess residual urine. To determine its amount, an ultrasound examination is performed.
The technique for its implementation is as follows:
- The subject drinks about one and a half liters of liquid 2 hours before the start of the study.
- At the first stage, ultrasound is performed with a full bladder.
- Then the patient is asked to urinate, after which the amount of urine remaining in the cavity of the organ is estimated.
This method is the most detailed and accurate.
I had to deal with this research method when my 4-year-old daughter complained of pain in her lower abdomen. The first phase of the study went well for us. Drinking a liter of juice for a child was not difficult. But when we were sent to the toilet, which was right there outside the door, problems began. In unfamiliar conditions, the child completely refused to urinate. We suffered for about 10 minutes before urination did happen. But due to the stressful environment for the child, apparently, the bladder was not completely emptied, and the residual urine in it was much higher than normal. Given the secondary importance of this particular method, we were not prescribed a second ultrasound, but the doctor admitted that the result could be questioned precisely because the child was too small and could not fully fulfill the necessary diagnostic conditions.
Principles of treatment depending on the causes
Treatment for excess residual urine is primarily to get rid of the causes that caused the pathology:
- In cystitis and other inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract, antibiotics are widely used to eliminate pathogenic microflora (penicillins - Amoxicillin, cephalosporins - Ceftriaxone). Ureaplasmosis and successfully treated with antimicrobial agents, in particular, Metronidazole.
- Therapy for prostatitis may also require application if the disease is caused by infectious agents. With prostate adenoma, the presence of tumor formations, it is possible to perform a surgical operation.
- The presence in the urinary tract of stones that impede the outflow of urine is an indication for taking antispasmodics (No-shpy), drugs that dissolve stones (Allopurinol). In exceptional cases, surgical intervention is possible.
- For problems with impaired innervation of the bladder, the following are indicated:
- taking anticholinergics (Atropine), which regulate the work of the sphincter of the organ;
- treatment with antidepressants for disorders of the nervous system;
- physiotherapy (electrophoresis), aimed at activating the reflex abilities of sphincters.
Photo gallery: medicines used for residual urine
 Amoxicillin is a broad-spectrum penicillin antibiotic.
Amoxicillin is a broad-spectrum penicillin antibiotic.  Metronidazole is an effective antimicrobial drug
Metronidazole is an effective antimicrobial drug  No-shpa relieves spasms of smooth muscles, facilitating urination with stones in the ureters and bladder
No-shpa relieves spasms of smooth muscles, facilitating urination with stones in the ureters and bladder  Allopurinol is a drug used primarily for high levels of uric acid in the blood to reduce the size and prevent the formation of stones in the urinary tract.
Allopurinol is a drug used primarily for high levels of uric acid in the blood to reduce the size and prevent the formation of stones in the urinary tract.  Atropine, like all anticholinergics, is designed to weaken or block the transmission of nervous excitation to the central nervous system (central nervous system)
Atropine, like all anticholinergics, is designed to weaken or block the transmission of nervous excitation to the central nervous system (central nervous system)
Is catheterization necessary and in what cases
If the amount of residual urine is too large due to the complete absence of urination, which may occur against the background of the presence of stones in the urinary tract or with advanced prostate adenoma in men, then it is necessary to carry out catheterization to remove it. The essence of this procedure is the introduction of a special catheter through the urethra into the bladder, through which the disturbed outflow of urine will resume. This procedure is performed exclusively in a hospital setting.
 Bladder catheterization is performed when the outflow of urine is completely obstructed
Bladder catheterization is performed when the outflow of urine is completely obstructed Treatment prognosis and possible complications
The prognosis of treatment depends directly on the cause that caused this pathology. With timely and adequately prescribed therapy, the prognosis in most cases is favorable: the elimination of the cause normalizes the processes of complete urine outflow.
Excess residual urine can cause serious complications:

In women, residual urine can cause infection and inflammation of the organs of the reproductive system.
Prevention measures
The basis for the prevention of residual urine is the timely diagnosis and treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract, prostatitis, urolithiasis. General recommendations include:
- compliance with the rules of personal hygiene;
- refusal of casual sexual relations;
- proper, balanced nutrition;
- physical activity.
Enriching the diet with foods that prevent the development of infection and have a diuretic property will help prevent bladder diseases:
- cranberry;
- cowberry;
- cucumbers;
- watermelon;
- melon;
- celery;
- lemon;
- ginger.
For the normal separation of urine, you should also not forget about the drinking regimen. At least 1.5 liters of clean water should be drunk per day.
Video: Bladder Protector Products
For any problems associated with pathologies of urination (itching, pain, pain, feeling of dissatisfaction after going to the toilet), you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. Such disorders respond well to therapy, but if left untreated, the likelihood of severe complications is very high.
Violation of the normal emptying of the organ intended for the accumulation of urine leads to the formation of residual urine in the bladder. As a result, the patient complains of a constant feeling that the bladder has not been completely emptied, because the volume of residual urine should normally not exceed 50 ml. In some cases, this sensation can be eliminated by additional tension in the abdominal muscles, sometimes even catheterization is required. The appearance of such a symptom indicates the need to contact a urologist who will prescribe an examination. If the patient has a lot of residual urine, this indicates the need for a thorough examination to identify hidden diseases.
Causes of residual urine in the bladder
The main reason that the amount of residual urine exceeds the norm is the weakening of a special muscle of the bladder - the detrusor (m. detrusor urinae), the tension of which leads to relaxation of the sphincter of the bladder and the beginning of the urination process. The following functional disorders or complications after previous diseases can contribute to the formation of residual urine in the bladder:
- benign prostatic hyperplasia - residual urine in adenoma is caused by squeezing the urethra by the prostate that is increasing due to neoplasm;
- persistent narrowing of the urethra (urethral stricture);
- the occurrence, due to inflammatory processes, of connective tissue scarring of the bladder neck (sclerosis of the bladder neck);
- fibrosis of the prostate (compression of the urethra and bladder neck);
- abnormal congenital folds in the urethra (urethral valve);
- neoplasms in the urethra;
- diseases of the spinal cord or brain;
- chronic urinary retention, which leads to an increase in the volume of residual urine, may be caused by damage to the nervous system;
- damage to the innervation system of the bladder, which can also manifest itself in urinary incontinence.
Why is residual urine dangerous?
Since the rate of residual urine should not exceed 50 ml, it is the excess of this indicator that will indicate to the doctor the need to identify the causes. Diagnosis of a symptom is simple - with a large volume, palpation and percussion of the suprapubic region are performed. In the event that the excess of the volume that the residual urine rate allows is insignificant, an ultrasound of the bladder is performed after urination.
Since residual urine is only a symptom of more serious diseases, the identification of this disorder requires the doctor to establish an accurate diagnosis and treatment of the primary disease, since this deviation can lead to:
- the occurrence of chronic pyelonephritis;
- the formation of kidney stones;
- the development of chronic urethritis;
- the appearance of vesicoureteral reflux;
- hydronephrosis;
- chronic renal failure .
Without the intervention of an experienced doctor, it is not possible to get rid of the formation of residual urine in the bladder, which can lead to much worse consequences.
Sometimes, after defecation, men get the feeling that emptying has not occurred completely. This phenomenon is often associated with chronic urinary retention syndrome. Residual urine in men is usually diagnosed when more than 50 ml of urine remains in the bladder after emptying. At times, the volume of residual urine is calculated in liters.
General picture of pathology
Pathologies of the male genitourinary system are a group of very unpleasant diseases that have similar symptoms. Feeling of incomplete urination also applies to such manifestations. In fact, the presence of residual urine is regarded by urologists as a genitourinary pathological sign, and not as a separate disease.
The main sign of residual urine is a feeling of incomplete emptying when urinating. A similar syndrome can be manifested by a two-stage urination process, and some men even need to make extra efforts, tensing their muscles in order to fully urinate. However, it happens that a man does not have any complaints about uncomfortable urination, although he has residual urine syndrome.
Common causes of residual urine
There can be many reasons for this condition:
- Benign hyperplastic changes in the tissues of the prostate, in other words, prostate adenoma;
- Urolithiasis, especially when stones are localized in the bladder cavity;
- Urethritis or inflammation of the urethra, narrowing or stricture of the urethra and other pathologies that lead to difficulty passing urine through the urethra;
- Cystitis of any origin and form;
- Tumor processes in the bladder of a malignant or benign nature such as polyps, cancer, leukoplakia, etc .;
- Innervation disorders of the pelvic organs;
- Pathologies of pelvic organs of an inflammatory nature, which are characterized by the presence of side effects such as bladder irritation.
In general, various kinds of obstruction of urination and neurogenic functional disorders lead to such a pathological condition. Since residual urine is regarded by specialists only as a pathological symptom, in the absence of therapeutic measures, such a phenomenon can provoke the development of many complications such as renal failure, pyelonephritis, hydronephrosis, vesicoureteral reflux, etc. Therefore, it is necessary to identify the causes of incomplete urination in time and eliminate them, then dangerous complications can be avoided.
Adenoma is to blame
 Benign prostatic hyperplastic processes are usually found in men over 45 and are manifested not only by urination disorders, but also by complete urination. Pathology is an uncontrolled growth of the gland, due to age-related changes in tissues with the formation of nodes, growths or seals in them, etc. A gradually formed formation increases in size, however, metastasis is not observed, because hyperplasia is of a benign nature.
Benign prostatic hyperplastic processes are usually found in men over 45 and are manifested not only by urination disorders, but also by complete urination. Pathology is an uncontrolled growth of the gland, due to age-related changes in tissues with the formation of nodes, growths or seals in them, etc. A gradually formed formation increases in size, however, metastasis is not observed, because hyperplasia is of a benign nature.
According to experts, the main provoking factor is age, with an increase in which the likelihood of adenoma increases. When the overgrown tissues compress the urination canal, the patient begins to be disturbed by the first manifestations of the disease - difficulty urinating and a feeling of incomplete emptying when urinating.
In addition, the patient complains of longer urination, increased urge (especially at night), a thin and sluggish stream with interruptions towards the end of the urination process. When the pathology is neglected, painful sensations appear in the lower abdomen, drip urination, painful ejaculation, difficulty with urination during urges, etc.
 Often the cause of residual urine is a neurogenic bladder - these are urinary disorders caused by disorders in the field of nervous system activity, which is responsible for urinary functions. The causes of a neurogenic bladder can be spinal lesions (hernias or vertebral pathologies, etc.), brain pathologies (strokes, hemorrhages or tumor processes, Parkinson's syndrome, etc.), HIV, peripheral nervous system lesions (for example, with diabetes or intoxication, etc.) .
Often the cause of residual urine is a neurogenic bladder - these are urinary disorders caused by disorders in the field of nervous system activity, which is responsible for urinary functions. The causes of a neurogenic bladder can be spinal lesions (hernias or vertebral pathologies, etc.), brain pathologies (strokes, hemorrhages or tumor processes, Parkinson's syndrome, etc.), HIV, peripheral nervous system lesions (for example, with diabetes or intoxication, etc.) .
Symptoms of a neurogenic (hyperactive) bladder are usually:
- Frequent calls;
- Incontinence;
- Night calls;
- Urine leakage;
- Feeling of incomplete emptying, etc.
Usually, the presence of residual urine indicates the presence of spinal lesions in the area just above the sacrum. As a result, there is a tension of the urethral sphincter, which makes the urination significantly more difficult. Treatment of a neurogenic bladder is based on a set of measures such as taking drugs that correct nervous system activity, physiotherapy sessions, forced urination with the help of tension in the muscle tissue of the press, exercise therapy, and surgical actions.
Urolithiasis disease
 One common cause of residual urine is cystolithiasis (or the formation of stones in the bladder), which is much more common in men. Such a pathology can develop for a number of internal or external reasons. Internal causes are caused by chronic infectious foci, material exchange pathologies such as gout, traumatic factors or heredity. External factors that provoke cystolithiasis are the wrong diet, physical inactivity, occupational hazards or drinking regimen.
One common cause of residual urine is cystolithiasis (or the formation of stones in the bladder), which is much more common in men. Such a pathology can develop for a number of internal or external reasons. Internal causes are caused by chronic infectious foci, material exchange pathologies such as gout, traumatic factors or heredity. External factors that provoke cystolithiasis are the wrong diet, physical inactivity, occupational hazards or drinking regimen.
Among the most characteristic manifestations of urolithiasis, pain in the half of the abdomen below the navel, radiating to the groin, perineum, or penis and scrotum, is particularly prominent. In the process of urination, a sudden interruption of the jet may occur, after which the excretion of urine stops, however, the man feels that the emptying of the bladder has not yet been completed. In other words, there is a pronounced syndrome of residual urine. If a man changes his body position, then urination may suddenly resume.
Treatment is based on the elimination of calculi, for which the patient can be prescribed stone-dissolving drugs that break down calculi into small particles, which are then naturally excreted along with urine. The technique of lithotripsy or crushing of stones is also popular. It is necessary to observe a specific diet, drinking regimen, rest and sanatorium treatment.
Urethral stricture
Residual urine often occurs with pathological narrowing of the urethra. Stricture processes are characterized by the replacement of normal mucous layers of the urethra with scar tissue. Such changes lead to significant violations in urination. Many reasons can cause the development of such a disease:
- Inflammatory genitourinary processes like urethritis, etc.;
- Burn damage to the urethra of a thermal or chemical nature;
- Impaired blood supply to the tissues of the urethra;
- Traumatic factors such as fractures of the penis or pelvic bones, trauma due to rough sex, blunt bruises of the perineum and groin, etc .;
- Oncological diseases, radiation treatment;
- Surgical errors such as unsuccessful surgery, unprofessional urological procedures (catheter placement, ureteroscopy, penis prosthesis, etc.);
- Congenital anomalies in the urethral structures.
In addition to residual urine, such a pathology is accompanied by difficulties and painful symptoms during urination, splashing of urine when emptying the bladder, a frequent desire to urinate, etc.
If the cause is cystitis
Often the causes of residual urine are the development of cystitis - this is a pathological condition of the bladder, for which the presence of inflammatory processes of various etiologies is typical. The causes of such a disease are quite numerous, however, the basis of the occurrence of cystitis is usually always an infection. Infection provocateurs can be gonococci, chlamydia, pathogenic fungi, staphylococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, etc.
These microorganisms can get into the bladder with the bloodstream, although there is also an ascending route of infection. Often, inflammation of the bladder occurs as a complication against the background of untreated or untreated pathologies such as urethritis, pyelonephritis or prostatitis, etc. Therefore, it is necessary to start treating various foci of an infectious nature in a timely manner.
Characteristic signs of cystitis are frequent desires to urinate (literally every quarter of an hour). At the same time, the portions of excreted urine are significantly reduced. When emptying the bladder, severe pain occurs, resembling a burning or cutting sensation. In addition, the man complains of pain in the penis and perineum. Often, the clinic of cystitis is supplemented by general organic intoxication.
Tumors of the bladder
Residual urine may also appear due to tumor processes in the bladder tissues. The reasons for this phenomenon often lie in harmful professional conditions, nicotine addiction, radiation exposure, chronic urination, etc. The malignant nature of the tumor can be indicated by hematuric symptoms, incontinence, pain in the bladder and groin. In addition, a man often begins to run out of need, and in the process of emptying the bladder, he feels a burning sensation, cutting soreness and discomfort. The excreted urine often becomes cloudy, and the general well-being of the patient worsens, hyperthermia and malaise appear, general weakness in the body.
Residual urine can be seen to result from a variety of genitourinary disorders. Since such a condition is fraught with various kinds of complications, it is necessary to contact a urologist at the first manifestations, who will identify the etiology of the syndrome and make the necessary appointments.
Attention. Only timely actions will help to quickly and without consequences solve the problem of incomplete emptying of the bladder, as well as avoid possible complications, both of the syndrome itself and the causes that caused it.
After each visit to the toilet, there is residual urine in the urea. This is a small amount of urine that remains in the bladder after urination and does not indicate pathology. If the volume increases, doctors talk about the beginning of pathological changes in the bladder or urethra and recommend that you undergo an examination. When a large amount of residual urine accumulates in the urea, a person has an unpleasant feeling of constant desire to urinate, and an effort must be made to push out the entire volume of urine.
Rates of residual urine in the bladder in men, women and children
Due to the fact that the structure and size of organs in each person is different and depends on the physique and heredity, the indicators will be individual and may vary. The rate of residual urine in men and women ranges between 40-45 ml. In children, this volume changes and increases with age. In a child, immediately after birth, residual urine is found in the amount of less than 3 ml. In one-year-old children, the volume of urine after being released from urine is up to 5 ml. In children at 4 years of age, the bladder contains up to 7 ml of urine after going to the toilet. In 10-year-old children, the amount of residual urine is up to 10 ml. With age, the bladder grows, and the volume of urine after urination increases and reaches a volume of 20 ml at the age of 15 years.
Causes of an increase in the residual urine in the urea
 Problems with the urea of a neurological nature may be due to vertebral hernias.
Problems with the urea of a neurological nature may be due to vertebral hernias. Neurological disorders occur with spinal injuries, tumors, spinal hernia. In adolescents, neurological disorders include congenital abnormalities in the work of the central nervous system. Inflammatory processes of an infectious nature push the body to pathological changes in the genitourinary system if a person has cystitis, balanitis or urethritis. In men, inflammatory processes in the prostate lead to the fact that the rest of the urine is not excreted from the urea. With inflammation, patients complain of frequent urge to empty the bladder, a weak stream of urine, the impossibility of urinating without effort. At the same time, patients are haunted by the feeling that the urea has not been completely emptied. Urolithiasis refers to obstructive causes of stagnation of urine. In the male half, stones form in the urinary tract, while in women they descend from the kidneys.
Diverticulum and - pathologies caused by the presence of other diseases that aggravate the situation.
Deviation symptoms
Symptoms that the remaining urine in the bladder has ceased to fall within the normal range are extensive and unpleasant. The very fact that a large volume of residual urine accumulates in the bladder indicates the passage of abnormal processes in the body. Added to this is the fact that the accumulation of urine causes pathologies and disorders in the functioning of the organs of the genitourinary system. The amount of urine remaining after urination helps determine the severity of abnormalities. The main symptom of the disease is a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. Other manifestations are associated with additional disorders and manifest themselves as:
 An additional symptom of pathology can be a jump in temperature.
An additional symptom of pathology can be a jump in temperature. - frequent desire to go to the toilet;
- unstable and scanty urine flow;
- making excessive efforts during the process of urination;
- the presence of blood inclusions in urine;
- pain syndrome during physical exertion;
- temperature jumps.
What is dangerous pathology?
If the first symptom occurs, you should seek help from a doctor and undergo a diagnosis. If you do not pay attention and start the disease, urine will stagnate in the bladder and pathogenic flora will begin to multiply in it. This will lead to the beginning of the infectious-inflammatory process. Additionally, with stagnation of urine, the chance of formation of calculi increases. Due to the increase in pressure, residual urine will rise to the kidneys and provoke:
- hydronephrosis;
- pyelonephritis;
- kidney failure.
How to determine the presence of pathology?
The purpose of the diagnosis is to correctly determine the residual urine. For this, the patient is asked about the manifestations that he had to face. Then he is prescribed a general analysis of urine and blood and a specific analysis to determine the presence of adenoma and prostate cancer. Instrumental research methods include procedures:
 Diagnosis of the disease can be done using cystometry.
Diagnosis of the disease can be done using cystometry. - orthostatic urine test;
- cystometry;
- electromyography;
- urethroprofilometry;
- Ultrasound of the urethra;
- Ultrasound of the prostate.
To determine the residual volume of urine (RVR), an ultrasound examination is performed in 2 stages. To begin with, a diagnosis is made with a full bladder. Then the patient is asked to empty the bladder and sit for 15 minutes, and then the changed organ is again examined on the monitor of the apparatus. The difference in size and volume, visible on ultrasound, is calculated according to the normative tables.
Treatment of the disease
The choice of treatment method determines the disease due to which urine remains in the urea. If the treatment is correct and the patient manages to achieve positive results, the residual urine in the bladder in men and women will no longer reach critical volumes and will return to normal. It is possible to eliminate the root cause that caused the deviation by using the following methods:
- conservative or surgical intervention to restore the patency of the urinary canals;
- relief of inflammation;
- restoration of the contractile muscles of the urinary system.
Residual urine is an important criterion for determining the presence of pathological changes in the lower urinary tract. In a healthy body in the cavity of the bladder after the act of urination, the residual urine should not exceed 10% of the total volume of urine. Determining the amount of residual urine in the bladder is of great diagnostic value in a number of pathologies, as a rule, requiring immediate treatment.
Mechanism of urination
The act of urination (innervation) is a combination of the work of the muscular layer (detrusor) of the bladder, which, by contracting, ensures the removal of fluid, and the sphincters of the urethra, which regulate the retention of urine in the process of its accumulation until the desire to perform the act of urination arises.
Depending on the development of pathological changes in any of the structural elements of the urinary tract responsible for the removal of urine, various disorders occur, leading to damage to the detrusor of the bladder, followed by the development of atrophy and, accordingly, the inability to contract sufficiently.
Important! Although the amount of urine in excess of 50 ml is of clinical importance, the maximum residual amount may exceed 1 liter.
Table: Permissible residual urine volume by age
The reasons
All the causes that cause the appearance of residual urine can be divided into several groups:
- neurological nature;
- inflammatory and infectious;
- obstructive;
- independent pathologies (diverticulum, urethral stricture).
Neurological disorders
Neurological disorders are always associated with a malfunction of that part of the nervous system that is responsible for three functions of the bladder:
- reservoir (a function that ensures the accumulation of urine in the cavity of the bladder);
- evacuation (a function that contributes to the removal of urine);
- valve (a function that allows you to keep a certain amount of urine in the bladder).
The defeat of any level of the nervous system - from the nerve endings located on the inner surface of the bladder, and ending with disorders in the brain, can lead to a number of abnormalities, including hyperfunction of the urethral sphincter. As a rule, the cause of the development of this pathology is damage to the spinal cord due to:
- tumor formations;
- intervertebral hernia;
- spinal injury;
- congenital pathology of the central nervous system (observed, as a rule, in a child).
Due to the difficulties that arise during urination, even with a full bladder, atony of the muscle layer develops, which, under constant pressure, loses the ability to contract and expel fluid, accumulating a large amount of residual urine.
Treatment of a neurogenic bladder consists in psychological, physical and drug methods of exposure:
- correction of the behavioral lifestyle (regulate the mode of drinking and urination);
- stimulation of urination by massaging the back area;
- physiotherapy;
- drug effect on weakening the tone of the sphincter;
- drugs that regulate the work of the central nervous system;
- physiotherapy.

Plexus of nerve endings in the lumbosacral region stimulates the process of urination
Inflammatory and infectious processes
As a rule, the role of inflammatory diseases in the formation of residual urine is the formation of urethral edema or sphincter spasm, due to soreness and tissue irritation. A similar reaction can be observed with cystitis, balanitis and urethritis. A separate place among inflammatory diseases that form a persistent violation of urination is occupied by inflammation of the prostate in men.
Enlargement of the prostate gland, due to an inflammatory process or the formation of a benign (prostatic hyperplasia) or malignant (prostate cancer) neoplasm, causes, at the initial stages of the development of the disease, minor urination disorders, subsequently leading to more pronounced:
- increased urge to go to the toilet;
- intermittency of the jet during urination;
- the need for tension of the press and straining for complete emptying of the bladder cavity;
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
Important! With a timely visit to a doctor, prostate adenoma is successfully treated with a complex effect of medications and physiotherapy procedures, and allows you to return to normal life.

Enlargement of the prostate towards the bladder, creating an obstruction to the outflow of urine
Obstruction of the urinary tract
The presence of stones in the bladder is one of the most common causes of residual urine. Cystoliosis occurs with equal frequency in both men and women. Only the mechanism of calculus formation differs - the formation of calculi directly in the cavity of the bladder is inherent in the male body, and the migration of stones from the kidneys is inherent in the female body.
The reasons for the formation of stones can be internal or external factors of influence:
- chronic infectious diseases of the urinary tract;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- improper diet;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- work in hazardous industries;
- improper drinking regime.
In addition to the main signs of the formation of residual urine, with cystoliosis, pain is noted in the lower abdomen with irradiation to the groin, scrotum, or perineum. Also a characteristic feature is a sharp interruption of a full-fledged jet during urination. Treatment consists in the elimination of stones with medications or lithotripsy, followed by their removal in a natural way.
Important! Therapy with stone-destroying drugs helps dissolve stones in the kidneys and bladder within 2-6 months, but has many side effects.

Canephron prevents the formation of calculi and has a minimum of contraindications
diverticulum
A diverticulum is a sac-like cavity formed from the wall of the bladder. There are two types of diverticula - true and false. A true diverticulum consists of the mucosal and muscular layer of the bladder tissue and is usually a congenital anomaly.
A false diverticulum (acquired) develops as a result of an increase in intravesical pressure that occurs against the background of pathological conditions accompanied by difficulty in urination and systematic incomplete emptying of the bladder. Due to the high pressure of the fluid, atrophy of the muscle layer develops, the destroyed fibers diverge, and the mucous membrane protrudes into the abdominal cavity under pressure.
The main difference between a false diverticulum and a true diverticulum is the absence of muscle fibers in the structure of its wall. The main clinical sign of a diverticulum is double urination with the appearance of cloudy urine.
Treatment consists, first of all, in the elimination of the causes that cause increased intravesical pressure (in case the diverticulum is acquired) and the subsequent surgical removal of the deformity.
Urethral stricture
Pathological narrowing of the urethra is called urethral stricture. Metaplasia of the tissues of the urethral mucosa can be caused by various causes that cause damage of varying severity:
- thermal or chemical burns of the urethra;
- inflammatory processes (cystitis, urethritis);
- injuries or bruises of the perineum;
- injury to the mucosa during the installation of the catheter;
- congenital pathologies of the urinary tract.
Due to the replacement of damaged cells with mucous connective tissue, scarring occurs, which significantly complicates the process of urination, as a result of which urine remains in the bladder.

Urethral stricture on x-ray
Signs and complications
Urine, which remains after urination in the cavity of the bladder, not only delivers a large amount of discomfort, but is itself an alarming symptom, the severity of which directly depends on its quantity.
Residual urine is an important clinical sign, as it leads to dysfunction of the upper urinary tract and is a consequence of pathological processes leading to functional disorders of the bladder.
The main symptoms that accompany excess residual urine are:
- increased urge to urinate;
- weak or intermittent jet;
- the need to tighten the abdominal muscles in order to start the process of urination or prevent its interruption;
- inflammatory processes in the urinary tract.
In the absence of timely treatment, the risk of developing inflammatory processes increases, since congestion creates a favorable environment for the development of pathogenic microflora and the formation of stones. Violation of the outflow of urine can also lead to the development of hydronephrosis, pyelonephritis and renal failure.

In the treatment of acute urinary retention, it is removed with a rubber catheter.
Diagnostics
Determining the presence and amount of residual urine is the main purpose of the examination, which includes asking the patient for clinically significant symptoms. Further, instrumental research methods are carried out, the list of which includes:
- study of the dynamics of changes in the pressure of the jet during urination (urofluometry);
- orthostatic urine test;
- measurement of pressure in the bladder at different moments of urination (cystometry);
- assessment of the contractility of the muscle layer of the bladder walls (electromyography);
- study of the functional state of sphincters and urethra (urethroprofilometry);
- Ultrasound of the bladder before and after urination;
- Ultrasound of the prostate.
Laboratory research methods:
- clinical analysis of urine (determination of the presence of bacteria, proteins and nitrogen in the urine);
- clinical blood test;
- determination of prostate specific antigen (PSA).
A reliable method for determining the amount of residual urine is the method of direct catheterization. But due to the difficulties associated with its implementation (invasiveness, risk of damage to the urethra, provocation of inflammatory processes), the assessment of the amount of residual urine is mainly carried out using ultrasound.
The diagnostic technique consists of two stages:
- Ultrasound of a full bladder.
- Ultrasound performed 10 minutes after urination.
At the same time, the dimensions of the three-dimensional image of the bladder and the length of its ultrasound shadow are estimated using mathematical formulas.
Important! In case of suspected presence of prostatic hyperplasia in men, the most informative diagnostic method is transrectal ultrasound.

Transrectal ultrasound technique
Since residual urine is only a symptom, the restoration of bladder detrusor function consists in treating the underlying disease and regularly removing urine using stimulating methods (washing with warm water, massage of the sacral spine, use of antispasmodics).
A positive effect can be achieved by using methods that improve blood circulation in the pelvic organs (aerobic exercise, walking, breathing exercises), relieve inflammation, and reduce the amount of fluid consumed before bedtime. In the vast majority, with a timely visit to a doctor, the tone of the muscle wall can be restored without the use of surgical methods of treatment.